Tensor 数据类型¶
参见
在计算机科学中,数据类型负责告诉编译器或解释器程序员打算如何使用数据。 参考 Data type WIKI.
MegEngine 中借助 numpy.dtype 来表示基础数据类型,参考如下:
NumPy 中有着专门实现的
numpy.dtype, 参考其对 Data type objects 的解释;NumPy 官方 Data types 文档中对数组类型和转换规则进行了解释。
根据 MEP 3 – Tensor API 设计规范 ,MegEngine 将参考《数组 API 标准》中对 数据类型 的规格定义。
上面提到的数据类型(Data type, dtype )是 Tensor 的一种基础属性,
单个 Tensor 内的元素的数据类型完全一致,每个元素占据的内存空间也完全相同。
Tensor 数据类型可以在创建时指定,也可以从已经存在的 Tensor 中指定进行转化,此时 dtype 作为参数使用 。
float32 是 MegEngine 中最经常用到的 Tensor 数据类型。
>>> a = megengine.functional.ones(5)
>>> a.dtype
numpy.float32
数据类型支持情况¶
在 MegEngine 中尚未支持《数组 API 标准》中需求的所有数据类型,目前状态如下:
数据类型 |
numpy.dtype |
等效字符串 |
数值区间 |
支持情况 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
布尔型 |
|
|
✔ |
|
有符号 8 位整型 |
|
\([-2^{7}, 2^{7}-1]\) |
✔ |
|
有符号 16 位整型 |
|
\([−2^{15}, 2^{15}-1]\) |
✔ |
|
有符号 32 位整型 |
|
\([−2^{31}, 2^{31}-1]\) |
✔ |
|
有符号 64 位整型 |
|
\([−2^{64}, 2^{64}-1]\) |
✖ |
|
无符号 8 位整型 |
|
\([0, 2^{8}-1]\) |
✔ |
|
无符号 16 位整型 |
|
\([0, 2^{16}-1]\) |
✖ |
|
无符号 32 位整型 |
|
\([0, 2^{32}-1]\) |
✖ |
|
无符号 64 位整型 |
|
\([0, 2^{64}-1]\) |
✖ |
|
半精度浮点 |
|
IEEE 754 1 |
✔ |
|
单精度浮点 |
|
IEEE 754 1 |
✔ |
|
双精度浮点 |
|
IEEE 754 1 |
✖ |
- 1(1,2,3)
IEEE. Ieee standard for floating-point arithmetic. IEEE Std 754-2019 (Revision of IEEE 754-2008), pages 1–84, 2019. doi:10.1109/IEEESTD.2019.8766229.
警告
并不是所有的已有算子都支持 MegEngine 数据类型之间的计算(仅保证 float32 类型全部可用)。
注解
我们会在 megengine.quantization 模块中提到对量化数据类型的支持。
dtype 作为参数使用¶
Tensor 初始化时以及调用 创建 Tensor 函数时可接受 dtype 参数,用来指定数据类型:
>>> megengine.Tensor([1, 2, 3], dtype="float32")
Tensor([1. 2. 3.], device=xpux:0)
>>> megengine.functional.arange(5, dtype="float32")
Tensor([0. 1. 2. 3. 4.], device=xpux:0)
如果使用已经存在的数据来创建 Tensor 而不指定 dtype, 则 Tensor 的数据类型将根据 默认数据类型 推导:
>>> megengine.Tensor([1, 2, 3]).dtype
int32
警告
如果使用不支持类型的 NumPy 数组作为输入创建 MegEngine Tensor, 可能会出现非预期行为。
因此最好在做类似转换时每次都指定 dtype 参数,或先转换 NumPy 数组为支持的数据类型。
另外还可以使用 astype 方法得到转换数据类型后的 Tensor(原 Tensor 不变):
>>> megengine.Tensor([1, 2, 3]).astype("float32")
Tensor([1. 2. 3.], device=xpux:0)
类型提升规则¶
注解
根据 MEP 3 – Tensor API 设计规范, 类型提升规则应当参考《数组 API 标准》 中的 相关规定 :

多个不同数据类型的 Tensor 或 Python 标量作为操作数参与运算时, 所返回的结果类型由上图展示的关系决定—— 沿着箭头方向提升,汇合至最近的数据类型,将其作为返回类型。
决定类型提升的关键是参与运算的数据的类型,而不是它们的值;
图中的虚线表示 Python 标量的行为在溢出时未定义;
布尔型、整数型和浮点型
dtypes之间未连接,表明混合类型提升未定义。
在 MegEngine 中,由于尚未支持《标准》中的所有类型,当前提升规则如下图所示:
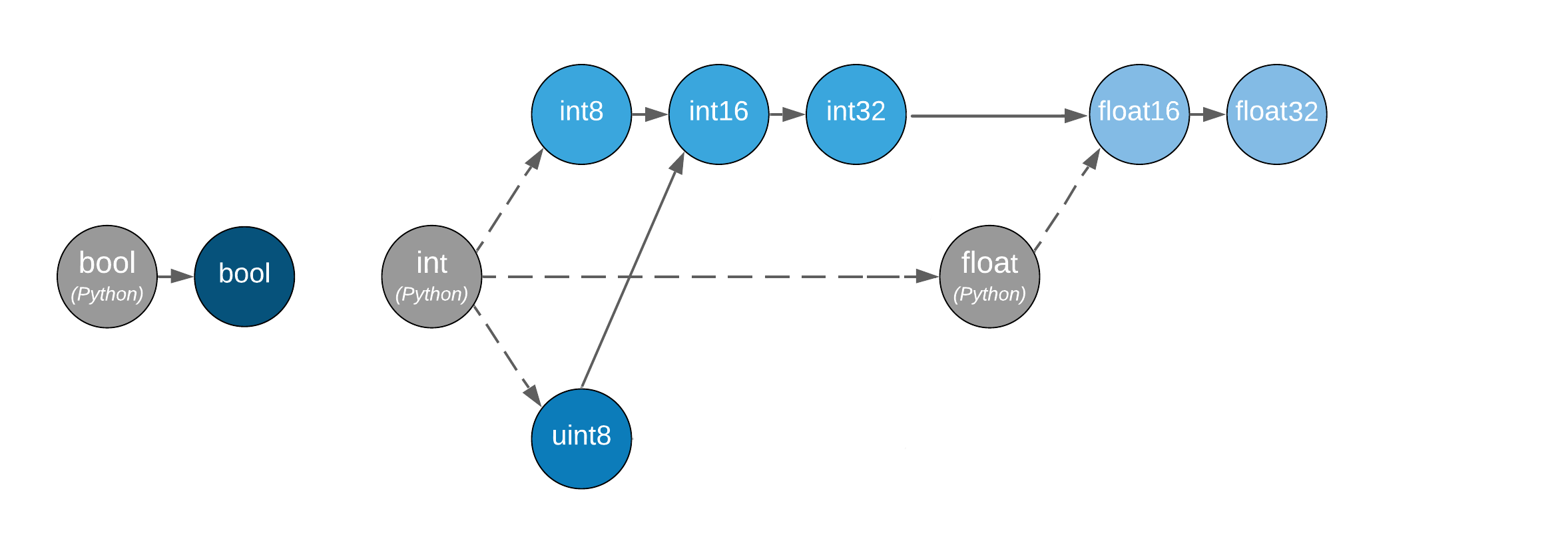
遵循 类型优先 的原则,存在 bool -> int -> float 的混合类型提升规则;
当 Python 标量类型与 Tensor 进行混合运算时,转换成 Tensor 数据类型;
布尔型
dtype与其它类型之间未连接,表明相关混合类型提升未定义。
注解
这里讨论的类型提升规则主要适用于 元素级别运算(Element-wise) 的情况。
举例如下, uint8 和 int8 类型 Tensor 运算会返回 int16 类型 Tensor:
>>> a = megengine.Tensor([1], dtype="int8") # int8 -> int16
>>> b = megengine.Tensor([1], dtype="uint8") # uint8 -> int16
>>> (a + b).dtype
numpy.int16
int16 和 float32 类型 Tensor 运算会返回 float32 类型 Tensor:
>>> a = megengine.Tensor([1], dtype="int16") # int16 -> int32 -> float16 -> float32
>>> b = megengine.Tensor([1], dtype="float32")
>>> (a + b).dtype
numpy.float32
Python 标量和 Tensor 混合运算时,在种类一致时,会将 Python 标量转为相应的 Tensor 数据类型:
>>> a = megengine.Tensor([1], dtype="int16")
>>> b = 1 # int -> a.dtype: int16
>>> (a + b).dtype
numpy.int16
注意,如果此时 Python 标量是 float 类型,而 Tensor 为 int, 则按照类型优先原则提升:
>>> a = megengine.Tensor([1], dtype="int16")
>>> b = 1.0 # Python float -> float32
>>> (a + b).dtype
numpy.float32
此时 Python 标量通过使用 默认数据类型 转为了 float32 Tensor.